Air pollution is a major global concern that poses significant risks to human health and the environment. To effectively address this issue, there is a growing need for advanced technologies that can accurately monitor and improve air quality. Gas sensors have emerged as a crucial tool in the field of air quality monitoring. By detecting and quantifying various types of gases, gas sensors provide valuable data for better understanding and management of air pollution. This article explores the significance of leveraging gas sensors for enhanced air quality monitoring, their applications, challenges, and future prospects.
The Importance of Air Quality Monitoring:
The monitoring of air quality is crucial for assessing the levels of pollutants present in the atmosphere and their impact on human health. Traditional monitoring methods often rely on large-scale monitoring stations, which may not capture localized variations in pollutant levels. Gas sensors, on the other hand, offer the advantage of real-time measurements at specific locations, providing a more accurate representation of air quality conditions.
Gas Sensor Technology:
Gas sensors employ various detection methods, including electrochemical, semiconductor, and optical techniques, to identify and measure specific gases. These sensors are designed to be highly sensitive, capable of detecting even trace amounts of pollutants. They have become smaller, more portable, and cost-effective, enabling widespread deployment in various settings such as homes, industries, and vehicles.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection:
Gas sensors enable real-time monitoring of air quality, providing continuous updates on pollutant levels. This real-time information is essential for immediate action when certain pollutant levels exceed acceptable thresholds. Gas sensor networks can be established to create a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics of air pollution, allowing for effective management strategies and interventions.
Indoor Air Quality Improvement:
Indoor air quality is equally important as outdoor air quality because people spend a significant amount of time indoors. Gas sensors play a vital role in monitoring indoor environments, alerting individuals to potential sources of pollutants such as chemicals, smoke, and mold. By identifying and addressing these issues promptly, gas sensors contribute to creating healthier indoor spaces.
Industrial Safety and Emission Control: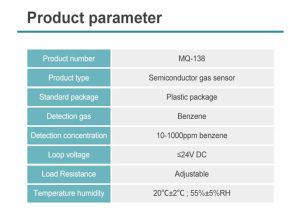
Gas sensors are widely utilized in industrial settings for safety and emission control purposes. They play a critical role in monitoring gases and detecting potential leaks, ensuring prompt action to prevent accidents and protect workers' safety. Gas sensors also aid in monitoring and controlling emissions from industrial processes, helping businesses comply with environmental regulations.
Smart Cities and Environmental Management:
As cities become more interconnected and smart technologies advance, gas sensors integrated into smart city infrastructures provide valuable data for urban planners and policymakers. This information aids in making informed decisions regarding urban development, transportation management, and environmental policies aimed at reducing pollution levels. Gas sensor networks can be combined with other data sources, such as weather information and traffic patterns, to gain insights into air quality patterns and develop targeted interventions.
Early Warning Systems and Emergency Response:
Gas sensors can be deployed as part of early warning systems to detect and preemptively respond to hazardous situations. For example, in the case of gas leaks or chemical spills, gas sensors can provide early detection, triggering alarms and evacuation procedures. This can significantly reduce the risks associated with such incidents, protecting human lives and minimizing damage to the environment.
Citizen Science and Public Engagement:
Gas sensors empower individuals to actively participate in monitoring air quality through citizen science initiatives. These initiatives often involve providing accessible and user-friendly gas sensor devices to community members. By collecting and sharing data, communities can contribute to a collective database of air quality measurements, fostering public awareness and encouraging local actions to improve air quality.
Conclusion:
Leveraging gas sensors for enhanced air quality monitoring offers numerous opportunities to mitigate the adverse impacts of air pollution. Real-time data collection, accurate measurements, and localized monitoring enable prompt action to safeguard human health and the environment. Gas sensors provide valuable information for decision-makers, aiding in the development of effective policies, interventions, and early warning systems. By embracing these advanced technologies and fostering partnerships between industries, governments, and communities, we can collectively work towards achieving cleaner air and a healthier
 : +86 155 8830 2704
: +86 155 8830 2704 : jxdziot@gmail.com
: jxdziot@gmail.com
