Indoor air quality (IAQ) is a crucial aspect of our overall well-being, as we spend a significant amount of time indoors. Poor IAQ can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems, allergies, and reduced productivity. With the rapid development of gas sensor technology, we now have powerful tools to monitor and improve indoor air quality effectively. In this article, we will explore the advancements in gas sensor technology and how they enhance IAQ monitoring.
Importance of Indoor Air Quality Monitoring:
Indoor air quality monitoring is essential for several reasons:
Health and Well-being: Good IAQ is vital for the health and well-being of building occupants. Monitoring IAQ helps identify potential pollutants and maintain a healthy indoor environment, reducing the risk of respiratory diseases, allergies, and other health issues.
Safety: Certain gases, such as carbon monoxide (CO) and radon, can be harmful or even fatal if present in high concentrations. Monitoring these gases ensures the safety of occupants and allows timely intervention if dangerous levels are detected.
Energy Efficiency: IAQ monitoring can be integrated with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to optimize energy consumption while maintaining good air quality. This integration allows for the adjustment of ventilation rates based on real-time IAQ data.
Advancements in Gas Sensor Technology:
Gas sensor technology has evolved significantly, leading to improved IAQ monitoring capabilities. The following advancements have played a vital role in enhancing indoor air quality monitoring:
Miniaturization and Portability:
Modern gas sensors have become smaller in size, more compact, and portable. This miniaturization allows for easy installation in various indoor settings, such as homes, offices, schools, and hospitals. Portable gas sensors can be carried around to measure air quality in different areas within a building, enabling targeted interventions when necessary.
Sensor Sensitivity and Selectivity: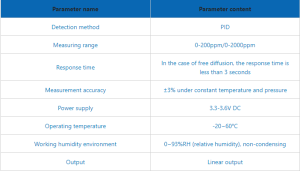
Advancements in gas sensor sensitivity and selectivity have significantly improved the accuracy of IAQ measurements. Sensors can now detect low concentrations of pollutants, even below regulatory thresholds. Moreover, they can differentiate between different gases, reducing the chances of false readings and ensuring reliable data.
Multi-Gas Detection:
Modern gas sensors are capable of detecting multiple gases simultaneously. Instead of relying on several individual sensors, a single multi-gas sensor can monitor various pollutants in real-time. This capability simplifies the monitoring process and reduces costs associated with multiple sensor installations.
Wireless Connectivity and IoT Integration:
Gas sensors now come with wireless connectivity options, allowing seamless integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. These connected sensors provide real-time data, enabling remote monitoring and control of indoor air quality from anywhere. Building managers and occupants can receive alerts and take necessary actions to maintain a healthy environment.
Data Analytics and Insights:
Advancements in data analytics have made it possible to derive valuable insights from IAQ monitoring data. Machine learning algorithms can process large volumes of data collected by gas sensors, identifying patterns, trends, and potential sources of indoor air pollution. These insights help in developing targeted strategies for improving IAQ and optimizing ventilation systems.
Applications of Advanced Gas Sensors in Indoor Air Quality Monitoring:
VOC and Formaldehyde Detection:
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and formaldehyde are common indoor air pollutants emitted by building materials, furniture, cleaning products, and other sources. Advanced gas sensors can detect and quantify these pollutants, allowing for prompt remedial actions and reducing exposure risks.
CO2 Monitoring for Ventilation Control:
Monitoring carbon dioxide (CO2) levels helps assess the adequacy of ventilation in indoor spaces. High CO2 concentrations indicate poor ventilation and the potential accumulation of other pollutants. Gas sensors can provide continuous CO2 measurements, enabling HVAC systems to adjust ventilation rates based on real-time IAQ data.
Radon Gas Detection:
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can seep into buildings from the ground. Prolonged exposure to high levels of radon increases the risk of lung cancer. Gas sensors equipped with radon detectors offer an effective means of monitoring radon concentrations and triggering mitigation measures when necessary.
Smart Home Integration:
Gas sensors can be integrated into smart home systems, allowing homeowners to monitor IAQ using their smartphones or voice assistants. Users can receive alerts, access historical data, and control ventilation systems remotely, ensuring a healthy living environment.
 : +86 155 8830 2704
: +86 155 8830 2704 : jxdziot@gmail.com
: jxdziot@gmail.com
