What is a VOC detector?
VOC detectors are programmed to detect small changes in specific gases and send the data to a central monitoring system. Plant personnel use these detectors to record and prevent any unexpected emissions spikes. Depending on the type of sensor used, a technician can calibrate each device to detect a specific VOC or group of compounds.
Due to the different layouts of different manufacturing plants and the specific VOCs emitted by each industry, custom installers are often developed for each plant. Professional technicians typically place sensors at various locations throughout the plant and connect them via fiber optic lines or wireless networks. To optimize results, detectors are located near leaks, pipe connections and vent valves.
Types of VOC detectors
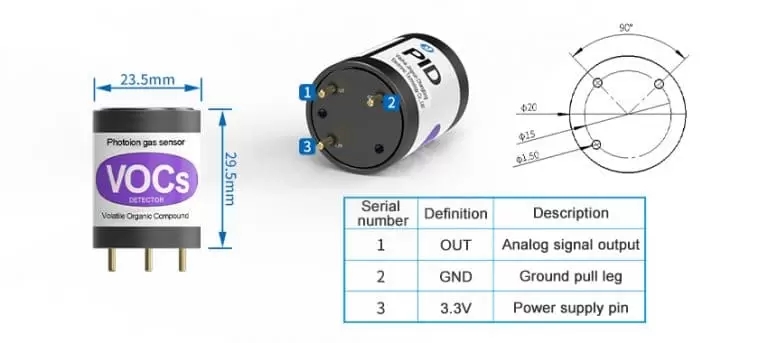
There are three main types of sensors used to detect VOC levels in the air: Photoionization Detectors (PID), Flame Ionization Detectors (FID), and Metal Oxide Semiconductor Sensors (MOS). Each sensor type is specifically designed to monitor specific compounds in different environments.
PID uses ultraviolet light to break down compounds into positive and negative ions to identify VOCs. These sensors can analyze and detect a wide range of chemicals, including methylene chloride.
FIDs are used to detect hydrocarbons in a variety of industries. The hydrogen flame interacts with hydrocarbons to produce ions. An alarm sounds when any change in ion levels is detected.
MOS sensors use delicate thin films to detect compounds in the surrounding atmosphere, such as benzene, ethanol and toluene. These sensors can work in low humidity.
A non-dispersive infrared carbon dioxide sensor (NDIR CO2 sensor) can also be used if desired. However, CO2 is not technically considered a VOC and is therefore not commonly used for VOC monitoring.

Sensor efficiency
VOC sensors would work more efficiently if the alarm system could be programmed specifically for each plant. By setting narrower detection parameters, plant personnel can obtain more accurate results and avoid false positives. Depending on the types of VOCs present and the area where the monitor is placed, targeted or mixed measurements can be made. Targeted measurements can be recorded more efficiently if specific VOCs are released and the exact emission parameters are known. Mixed VOC measurement is more suitable for open-air environments where various VOCs are detected.
 : +86 155 8830 2704
: +86 155 8830 2704 : jxdziot@gmail.com
: jxdziot@gmail.com
