Indoor air quality (IAQ) has a profound impact on our health and overall well-being. With the majority of our time spent indoors, it is essential to ensure that the air we breathe is clean and free from harmful pollutants. The use of advanced gas sensors has emerged as a powerful solution to enhance IAQ by accurately detecting and monitoring various gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This article explores the role of advanced gas sensors in enhancing IAQ, their applications, and the benefits they bring to indoor environments.

Understanding Indoor Air Quality:
Indoor air quality refers to the condition of the air within buildings, including homes, offices, schools, and public spaces. Poor IAQ can result in adverse health effects, such as respiratory problems, allergies, fatigue, and even more serious conditions like asthma. IAQ is influenced by various factors, including outdoor pollution sources, building materials, ventilation systems, human activities, and the presence of pollutants and VOCs.
Traditional Monitoring Challenges:
Traditionally, IAQ monitoring has relied on periodic sampling and laboratory analysis, which is time-consuming and provides limited data. This approach fails to capture real-time fluctuations in pollutant levels and cannot provide immediate alerts or corrective actions. Additionally, it does not consider the spatial variations of IAQ within a building, as pollutant levels can vary significantly from one area to another.
Advanced Gas Sensors for IAQ:
Advanced gas sensors have revolutionized IAQ monitoring by providing real-time, continuous measurements of various gases and VOCs. These sensors utilize cutting-edge technologies like electrochemical and photoionization detection to detect and quantify specific pollutants present in the air. They are capable of measuring gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM).
Applications of Advanced Gas Sensors in Enhancing IAQ:
Ventilation Control: Gas sensors play a crucial role in optimizing ventilation systems by continuously monitoring CO2 levels. High CO2 levels indicate poor air circulation, inadequate ventilation, or overcrowding. By integrating gas sensors with intelligent ventilation systems, fresh air intake can be adjusted based on real-time measurements, ensuring optimal air quality and energy efficiency.
VOC Detection: Advanced gas sensors can detect and quantify harmful VOCs emitted from building materials, furniture, cleaning products, and other sources. These sensors enable the identification of specific VOCs and their sources, allowing for targeted actions to reduce exposure. This is particularly important in confined spaces where VOCs can accumulate and pose health risks.
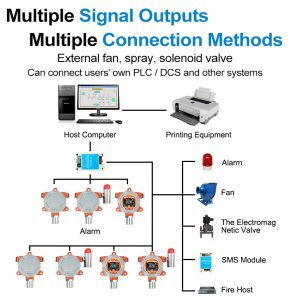
Air Purification Systems: Gas sensors are used in conjunction with air purification systems to assess the effectiveness of filtration and purification processes. By continuously monitoring pollutant levels, these sensors can trigger the activation of purification systems when pollutant concentrations exceed acceptable limits. This ensures that the air is efficiently purified, reducing the risk of respiratory problems and allergies.
Early Warning Systems: Gas sensors provide early warning alerts in the event of gas leaks, such as carbon monoxide or natural gas. These timely warnings allow occupants to evacuate safely and alert authorities or emergency services. By integrating gas sensors with alarm systems, potential hazards can be detected and addressed promptly, preventing accidents and potential loss of life.
Benefits of Advanced Gas Sensors for IAQ:
Health and Well-being: By accurately detecting and monitoring pollutants and VOCs, gas sensors contribute to maintaining a healthy indoor environment. This directly improves the well-being and productivity of occupants, particularly in settings like schools, offices, and healthcare facilities.
Energy Efficiency: Advanced gas sensors help optimize ventilation systems, ensuring that fresh air is supplied only when necessary. By reducing unnecessary air exchange, energy consumption is minimized, resulting in energy savings and reduced carbon footprint.
Preventive Maintenance: Continuous monitoring of IAQ using gas sensors allows for proactive maintenance of HVAC systems, preventing the buildup of pollutants, mold, and other contaminants. This extends the lifespan of equipment and reduces maintenance costs.
Regulatory Compliance: Gas sensors assist in achieving and maintaining compliance with IAQ regulations and standards. Real-time measurements provide a comprehensive overview of IAQ conditions, making it easier to demonstrate adherence to guidelines.
Environmental Impact: By promoting healthy indoor environments, advanced gas sensors contribute to sustainable living and environmental protection. Reduced exposure to pollutants and VOCs minimizes their emission
 : +86 155 8830 2704
: +86 155 8830 2704 : jxdziot@gmail.com
: jxdziot@gmail.com
