With the rapid urbanization and industrialization of cities around the world, monitoring and managing urban environmental quality have become critical tasks. Gas sensors play a pivotal role in urban environmental monitoring by providing real-time data on air pollution, enabling authorities to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions. This article explores the significance of gas sensors in urban environmental monitoring, their applications, and the benefits they bring to cities.
Understanding Urban Environmental Monitoring:
Urban environmental monitoring refers to the systematic collection and analysis of data on various environmental parameters within urban areas. These parameters include air quality, water quality, noise levels, temperature, humidity, and more. Monitoring urban environments is essential as cities face numerous environmental challenges, including air pollution, water contamination, and noise pollution. By collecting accurate and reliable data, policymakers and environmental agencies can identify problem areas, assess the effectiveness of environmental initiatives, and implement appropriate strategies to mitigate environmental risks.
The Role of Gas Sensors:
Among the various parameters monitored in urban environments, air quality is of paramount importance due to its direct impact on public health. Gas sensors serve as key tools in monitoring air pollution, specifically by measuring the concentration of gases and pollutants present in the atmosphere. They detect and quantify gases such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM). By continuously monitoring these gases, gas sensors provide valuable insights into the level of air pollution and its composition, enabling authorities to take appropriate measures to reduce pollution levels and protect public health.
Applications of Gas Sensors in Urban Environmental Monitoring:
Air Quality Monitoring: Gas sensors are extensively used to monitor air quality in urban areas. They are deployed in fixed stations and mobile platforms, such as vehicles and drones, to collect real-time data on pollutant concentrations. This data helps in identifying pollution hotspots, assessing the impact of industrial activities, and evaluating the effectiveness of pollution control measures.
Traffic Management: Gas sensors can be integrated into intelligent transportation systems to monitor and manage traffic-related emissions. By detecting and quantifying pollutants emitted by vehicles, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO), gas sensors provide valuable insights for optimizing traffic flow, implementing emission reduction strategies, and planning alternative transportation routes.
Industrial Emission Monitoring: Gas sensors play a crucial role in monitoring emissions from industrial facilities. By continuously measuring the concentration of pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), gas sensors help ensure compliance with regulatory standards. They also assist in identifying sources of pollution, implementing corrective measures, and promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Indoor Air Quality: In addition to outdoor air monitoring, gas sensors are used to monitor indoor air quality in urban settings. Indoor environments, such as homes, offices, schools, and public spaces, can be affected by pollutants released from building materials, cleaning products, and human activities. Gas sensors detect harmful gases and VOCs indoors, allowing for timely actions to improve ventilation, reduce exposure, and create healthier indoor environments.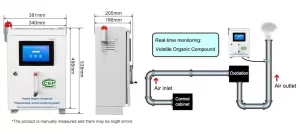
Benefits of Gas Sensors for Urban Environmental Monitoring:
Early Warning and Public Health Protection: Gas sensors provide real-time data on pollutant concentrations, enabling authorities to issue early warnings and take immediate actions during episodes of high pollution levels. This helps protect public health and mitigate the risks associated with prolonged exposure to pollutants.
Effective Pollution Control: Gas sensors assist in formulating and implementing effective pollution control strategies. Real-time data obtained from gas sensors helps policymakers evaluate the impact of pollution control measures, identify sources of pollution, and make informed decisions to reduce emissions.
Smart City Integration: Gas sensors can be integrated into smart city frameworks, facilitating data sharing and analysis. By combining gas sensor data with other environmental monitoring data, urban planners can gain a comprehensive understanding of the overall environmental conditions and make data-driven decisions for sustainable development.
Environmental Regulation Compliance: Gas sensors help industries and businesses monitor their emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. This enables proactive management of pollution sou
 : +86 155 8830 2704
: +86 155 8830 2704 : jxdziot@gmail.com
: jxdziot@gmail.com
